The treatment of gymnastics injuries depends on the specific type and severity of the injury.
However, common principles of treatment include…
- Rest – Rest is essential to allow the injured tissues to heal. Depending on the severity of the injury, this may involve temporarily discontinuing gymnastics activities or modifying training routines to avoid aggravating the injury.
- Ice – Applying ice to the injured area can help reduce pain and inflammation. Ice should be applied for 15-20 minutes every 2-3 hours during the initial stages of injury.
- Compression – Compression bandages or wraps may be used to help reduce swelling and provide support to the injured area. It’s important not to wrap too tightly, as this can impair circulation.
- Elevation – Elevating the injured limb above the level of the heart can help reduce swelling by promoting drainage of excess fluid from the injured tissues.
- Pain Management – Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be used to alleviate pain and discomfort. However, it’s important to follow dosing instructions and consult a healthcare professional if pain persists or worsens.
- Physical Therapy – Once the acute phase of injury has passed, physical therapy may be recommended to help restore strength, flexibility, and range of motion to the injured area. Physical therapists can design individualized exercise programs to address specific weaknesses or imbalances and facilitate safe return to gymnastics activities.
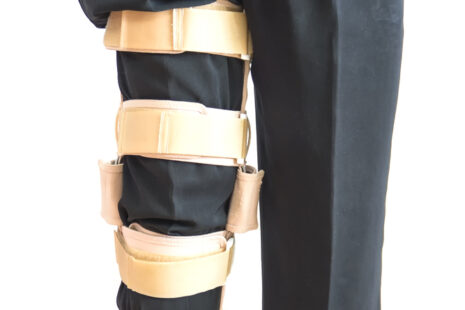
- Bracing or Supportive Devices – In some cases, supportive braces, splints, or orthotic devices may be used to provide stability and protection to the injured area during the healing process.
- Medical Intervention – For more severe injuries, such as fractures, ligament tears, or dislocations, medical intervention may be necessary. This may include immobilization with a cast or splint, surgical repair, or other specialized treatments depending on the nature of the injury.
- Rehabilitation – Following the acute phase of injury and initial treatment, a structured rehabilitation program may be prescribed to gradually reintroduce gymnastics-specific activities and movements while minimizing the risk of reinjury.
- Prevention Strategies – Once the injury has healed, it’s important to implement preventive measures to reduce the risk of future injuries. This may include proper warm-up and stretching, strength and conditioning exercises, technique refinement, and adherence to safety guidelines and equipment recommendations.
It’s essential to seek medical evaluation and guidance for any gymnastics-related injury to ensure appropriate diagnosis and treatment. Athletes should follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations and gradually progress back to full activity levels under their supervision to minimize the risk of reinjury.