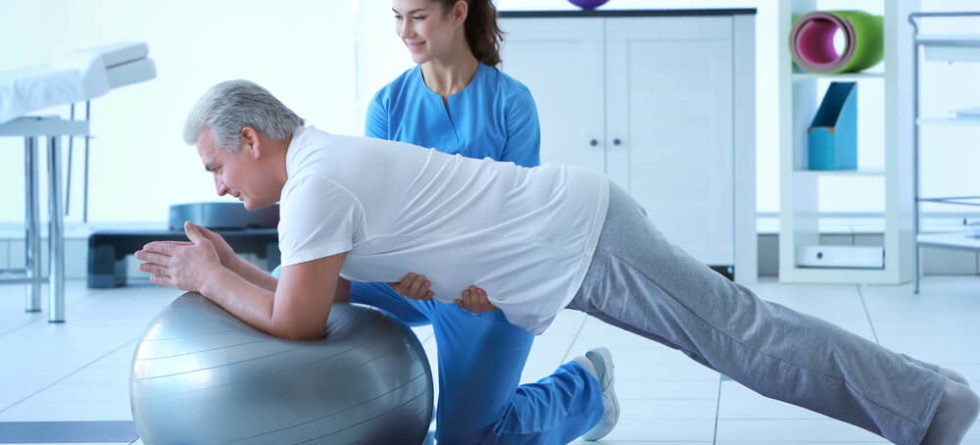
Spinal manipulation, also known as spinal mobilization or manual therapy, is a hands-on technique performed by physical therapists to address musculoskeletal issues, including those related to the spine. It involves skilled movements of the therapist’s hands to apply controlled forces to the joints, soft tissues, and muscles around the spine. The primary goals of spinal manipulation are to improve joint mobility, reduce pain, and restore function.
How a physical therapist performs spinal manipulation…
- Assessment – Before performing spinal manipulation, the physical therapist will conduct a thorough assessment of your condition. They will evaluate your range of motion, joint mobility, muscle strength, and any areas of pain or discomfort to identify the source of the problem.
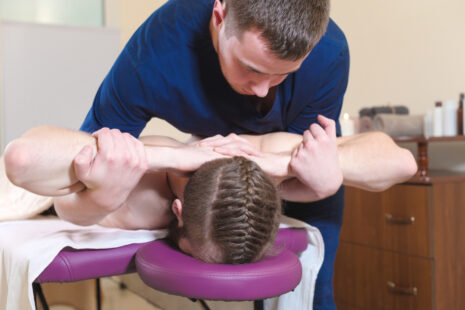
- Patient Positioning – You may be asked to lie on a treatment table, face up, face down, or on your side, depending on the area of the spine that needs to be treated.
- Preparation – The physical therapist will explain the procedure and ensure you are comfortable. They may also apply heat or use other techniques to warm up the tissues and muscles around the spine, making them more responsive to manipulation.
- Application of Techniques – Using their hands, the physical therapist will apply gentle, controlled force to the affected joint or area of the spine. The goal is to restore normal joint motion, reduce stiffness, and relieve pressure on nerves or soft tissues.
- Types of Spinal Manipulation – There are various techniques for spinal manipulation used by physical therapists, including high-velocity low-amplitude (HVLA) thrusts, sustained pressure or mobilization, and other specialized methods tailored to the patient’s needs.
- Patient Feedback – Throughout the procedure, the physical therapist will communicate with you to ensure the manipulation is well-tolerated and to gather feedback about any changes in symptoms or sensations.
- Post-treatment Care – After spinal manipulation, the therapist may provide additional treatments, such as therapeutic exercises, to reinforce the manipulation’s benefits and support long-term recovery.