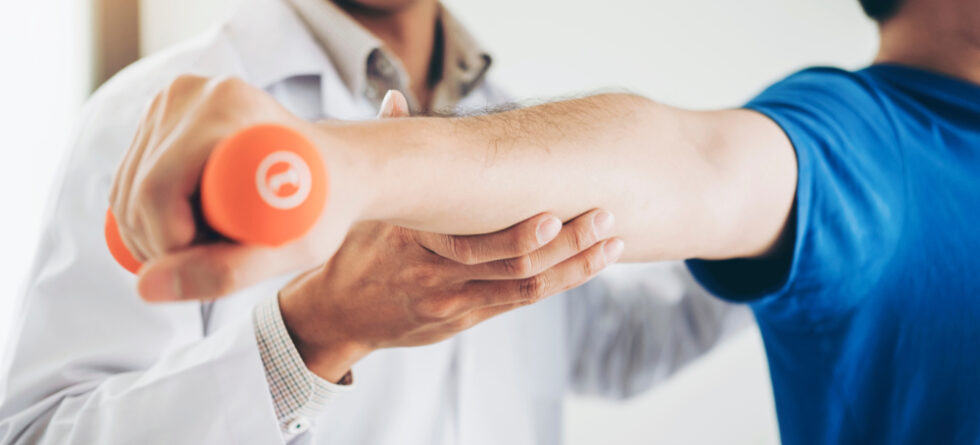
Rehabilitating a shoulder injury without surgery is often possible, especially for mild to moderate injuries or conditions. Non-surgical treatment options focus on reducing pain, improving range of motion, and strengthening the muscles around the shoulder to support and stabilize the joint. The approach to rehabilitation will depend on the specific type and severity of the injury, as well as the individual’s overall health and activity level.
Here’s an overview of strategies for rehabilitating a shoulder without surgery…
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
- Rest and Activity Modification – Initially, resting the injured shoulder and avoiding activities that exacerbate pain is crucial. Modifying daily activities to prevent further injury can also be helpful.
- Physical Therapy – A cornerstone of non-surgical shoulder rehabilitation, physical therapy involves exercises tailored to strengthen the shoulder, improve flexibility, and restore range of motion. A physical therapist will design a program suited to the individual’s specific needs.
- Cold and Heat Therapy – Applying ice packs can help reduce inflammation and pain in the acute phase of an injury. Later, heat therapy may be used to relax and loosen tissues and stimulate blood flow to the area.
- Pain Management – Over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications can be used to manage pain and reduce inflammation. In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be recommended to decrease inflammation and pain.
- Supportive Devices – Slings or braces may be used temporarily to immobilize the shoulder and allow it to heal, especially in cases of significant pain or instability.
Physical Therapy Exercises
- Range of Motion Exercises – Gentle stretching exercises can help restore flexibility and range of motion in the shoulder.
- Strengthening Exercises – As pain decreases, exercises to strengthen the shoulder muscles, including the rotator cuff and scapular stabilizers, are gradually introduced.
- Posture Training – Correcting posture and learning proper body mechanics play a crucial role in preventing future shoulder problems.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Ergonomic Adjustments – Making changes to work and home environments to reduce strain on the shoulder can help prevent re-injury.
- Activity Pacing – Learning to pace activities and take breaks can prevent overuse and fatigue of the shoulder muscles.
Expectations for Recovery
- Time Frame – The time needed for recovery varies widely depending on the nature and severity of the injury. Mild injuries may improve within a few weeks, while more severe conditions can take several months to rehabilitate fully.
- Commitment to Rehabilitation – Consistency in performing prescribed exercises and adhering to recommended lifestyle modifications is critical for effective recovery.
- Follow-Up Care – Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is important to monitor progress and adjust treatment plans as needed.
While surgery may be necessary for severe shoulder injuries, many shoulder conditions can be effectively rehabilitated without surgical intervention. A combination of rest, physical therapy, medication, and lifestyle modifications offers a holistic approach to recovery. It’s vital to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses the specific needs and goals of the individual. With patience and dedication to the rehabilitation process, many people can achieve pain relief and return to their normal activities.